Risk management is one the most important internal processes both in PKO Bank Polski SA and in other entities of the PKO Bank Polski SA Group. Risk management aims at ensuring profitability of business activity, with ensuring control of risk level and maintaining it within the risk tolerance and limits system applied by the Bank and the Group, in the changing macroeconomic and legal environment. The level of the risk plays an important role in the planning process.
In the PKO Bank Polski SA Group, the following types of banking risk have been identified, which are subject to management: credit risk, interest rate risk, currency risk, liquidity risk, commodity price risk, price risk of equity securities, derivative instruments, operational risk, compliance risk, macroeconomic changes risk, model risk, business risk (including strategic risk), loss of reputation risk, capital risk and insurance risk.
52.1. Elements of banking risk management process
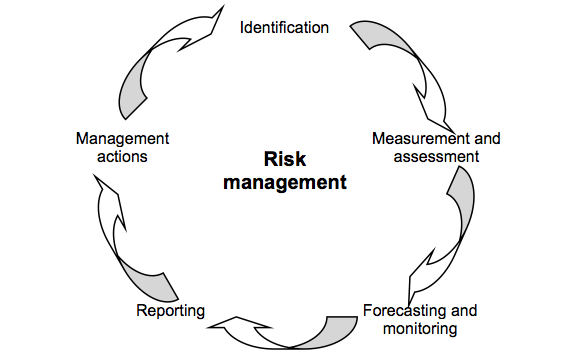
The process of banking risk management in the Group consists of the following stages:
- risk identification:
the identification of actual and potential sources of risk and estimation of the significance of the potential influence of a given type of risk on the financial situation of the Group. Within the risk identification process, types of risk perceived as material in the Bank’s activity, the entities of the Group and the whole Group’s activity are identified,
- risk measurement and assessment:
risk measurement covering defining risk assessment measures adequate to the type and significance of the risk, data availability and quantitative risk assessment by means of determined measures, as well as risk assessment aimed at identifying the scale or scope of risk, taking into account the achievement of goals of risk management. Within risk measurement, stress-test are being conducted on the basis of assumption providing a fair risk assessment,
- risk forecasting and monitoring:
preparing risk level forecasts and monitoring deviations from forecasts or adopted reference points (e.g. limits, thresholds, plans, measurements from the previous period, issued recommendations and suggestions). Risk monitoring is performed with the frequency adequate to the materiality and volatility of a specific risk type,
- risk reporting:
periodic informing the authorities of the Bank about the results of risk measurement, taken actions and actions recommendations. Scope, frequency and the form of reporting are adjusted to the managing level of the recipients,
- management actions:
including, particularly, issuing internal regulations, establishing the level of risk tolerance, establishing limits and thresholds, issuing recommendations, making decisions about the use of tools supporting risk management. The objective of taking management actions is to form the risk management and the risk level.
The risk management process is described on the chart below:
52.2. Main principles of risk management
Risk management in the Group is based especially on the following principles:
- the Group manages all of the identified types of banking risk,
- the risk management process is appropriate to the scale of the operations and to the materiality, scale and complexity of a given risk and tailored to new risk factors and sources on a current basis,
- the risk management methods (in particular the models and their assumptions) and the risk measurement systems are tailored to the scale and complexity of the risk and verified and validated on a periodical basis,
- the area of risk and debt recovery remains organisationally independent from business activities,
- risk management is integrated with the planning and controlling systems,
- the risk level is monitored on a current basis,
- the risk management process supports the implementation of the Group’s strategy in keeping with the risk management strategy, in particular with regard to the level of tolerance of the risk.
52.3. The organisation of risk management in the Bank
Risk management in the Bank takes place in all of the organisational units of the Bank.
The organisation of risk management is presented in the chart below:
The organisation of risk management chart
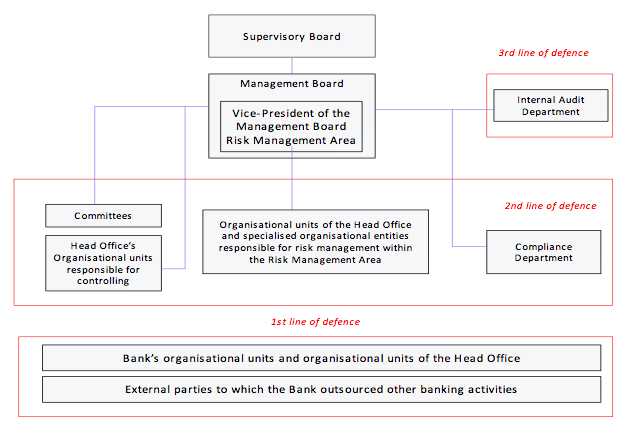
The risk management process is supervised by the Supervisory Board of the Bank, which is informed on a regular basis about the risk profile of the Bank as well as of the PKO Bank Polski SA Group and the most important activities taken in the area of risk management.
The Bank’s Management Board is responsible for the risk management, including supervising and monitoring of activities taken by the Bank in the area of risk management. The Bank’s Management Board takes the most important decisions affecting the risk profile of the Bank and adopts internal regulations defining the risk management system.
The risk management process is carried out in three, mutually independent lines of defence:
- the first line of defence, which is functional internal control that ensures using risk controls mechanisms and compliance of the activities with the generally applicable laws,
- the second line of defence, which is the risk management system, including methods, tools, process and organisation of risk management,
- the third line of defence, which is an internal audit.
The independence of the lines of defence consists of preserving organisational independence in the following areas:
- the function of the second line of defence as regards creating system solutions is independent of the function of the first line of defence,
- the function of the third line of defence is independent of the functions of the first and second lines of defence,
- the function of managing the compliance risk reports directly to the President of the Management Board.
The first line of defence is being performed in particular in the organisational units of the Bank, the organisational units of the Head Office and entities of the Group and concerns the activities of those units, cells and entities which may generate risk. The units, cells and entities of the Group are responsible for identifying risks, designing and implementing appropriate control mechanisms, unless control mechanisms have been implemented as part of the measures taken in the second line of defence. At the same time the Group entities are obliged to have comparable and cohesive systems of risk evaluation and control in the Bank and in the Group entities, taking into account the specific business characteristic of each entity and the market on which it operates.
The second line of defence is being performed, in particular, in the Risk Management Area, the organisational unit of the Head Office managing the compliance risk, reputation risk, respective committees as well as the organisational units of the Head Office responsible for controlling.
The third line of defence is being performed as part of internal audit, including the audit of the effectiveness of the system of managing the risk.
The organisational units of the Head Office of the Bank that constitute the Banking Risk Division, the Department of Risk Integration, the Department of Restructuring and Debt Collection of the Corporate Client, and the Analysis and Credit Risk Assessment Centre, as well as Restructuring and Debt Collection Centre, manage risk within the limits of competence assigned to them.
The Banking Risk Division is responsible in particular for:
- identifying risk factors and sources,
- measuring, assessing, monitoring and reporting risk levels (material risks) on a regular basis,
- measuring and assessing capital adequacy,
- preparing recommendations for the Management Board or committees regarding the acceptable level of risk,
- creating internal regulations on managing risk and capital adequacy,
- developing IT systems designated to support risk and capital adequacy management.
The Department of Risk Integration is responsible in particular for:
- validation of risk models,
- implementation of effective system of the model risk management in the Group,
- coordinating the implementation of integrated risk management system in the Group,
- supervision over risk management in the Group.
The Department of Restructuring and Debt Collection of the Corporate Client is responsible in particular for:
- recovering receivables from difficult corporate clients effectively, with the amount not less than the value specified in separate internal regulations of the Bank, through their restructuring and debt collection,
- protection of the Bank’s interests as a creditor in the course of compulsory pursuing claims,
- selling receivables effectively and acquisition of assets as a result of pursuing claims,
review and classification of receivables being managed within the Department and off-balance sheet liabilities granted as well as determination of their impairment allowances associated with the risk of Bank’s activities.
The Restructuring and Debt Collection Centre is responsible in particular for:
- recovering receivables from difficult clients effectively through their restructuring and debt collection and increasing the effectiveness of such actions,
- effective monitoring of delays in the collection of receivables from retail market clients,
- effective outsourcing of the tasks carried out, as well as effective management of assets taken over as a result of recovering the Bank’s receivables,
- selling difficult receivables effectively.
The objective of the Analysis and Credit Risk Assessment Centre is the reduction of credit risk of individual credit exposures of the Bank’s retail market clients, corporate market clients and financial institutions, which are significant particularly due to the scale of exposure, client segment or risk level and ensuring effective credit analyses in respect of mortgage loans granted to individual clients through the Bank’s retail network and loans granted to small and medium enterprises clients evaluated with rating methods, as well as taking credit decisions in this respect.
Risk management is supported by the following committees:
The Risk Committee (‘the RC’):
- monitors the integrity, adequacy and efficiency of the bank risk management system, as well as capital adequacy and implementation of the risk management policies binding in the Bank consistent with the Bank’s Strategy,
- analyses and evaluates the application of strategic risk limits specified in the PKO Bank Polski SA’s Bank Risk Management Strategy,
- supports the Supervisory Board in the banking risk management process by formulating recommendations and making decisions concerning capital adequacy and the efficiency of the banking risk monitoring system.
The Assets & Liabilities Management Committee (‘the ALCO’):
- makes decisions within the scope of limits and thresholds on particular types of risks, issues related to transfer pricing, models and portfolio parameters used to determine impairment allowances and provisions, as well as other significant financial and business risk models and their parameters,
- gives recommendations to the Management Board i.a. with regard to determining the structure of the Bank’s assets and liabilities, managing different types of risk, equity and price policy.
The Bank’s Credit Committee (‘the BCC’):
- makes loan decisions with regard to significant individual loan exposures and credit risk models,
- issues recommendations in the above-mentioned respect to the Management Board,
- makes decisions regarding the approval of credit risk models and results of validation of these models in the composition including the representants of Finance and Accounting Area.
The Central Credit Committee (‘the CCC’) and credit committees which operate in the corporate macro-regions.
supports the decisions taken by the relevant Division directors and the Management Board members with its recommendations and the credit committees operating in the regions support directors of the corporate macro-regions in matters bearing a higher risk.
The Operating Risk Committee (‘the ORC’):
- takes decisions, issues recommendations and opinions regarding i.a. strategic tolerance limits and loss limits for operational risk, key risk indicators (KRI), assumptions of stress-tests, results of validation of operational risk measurement models, changes in AMA approach and taking actions to reduce the level of operational risk in all areas of the Group’s activities,
- prepares operating risk management recommendations for the PKO Bank Polski SA Group entities, which are submitted to the PKO Bank Polski SA Group entities as a part of the Bank’s corporate governance over those entities.
ALCO, RC, ORC, BCC, the Management Board and the Supervisory Board are recipients of cyclic reports concerning the individual risk types.
52.4. Activities in the area of risk management in the Group
The Bank supervises activities of the individual subsidiaries of the PKO Bank Polski SA Group. As part of this supervision, the Bank sets out and approves their development strategies, including the level of the risk. The Bank also supervises the entities’ risk management systems and provides support in the development of these systems. Additionally, it reflects business risk level of the particular entities in the risk reporting and monitoring system of the entire Group.
The internal regulations concerning management of certain types of risk in the entities of the Group are defined by internal regulations implemented by those entities, after consulting the Bank’s opinion and having taken into account the recommendations issued to the entities by the Bank. The internal regulations of the entities concerning risk management allow for consistent and comparable assessment of particular types of risk within the Bank and entities of the Group, as well as reflect the extent and nature of the relationship of entities included in the Group, the nature and scale of the entity’s activity and the market on which it operates.
The risk management in the Group entities is carried out in particular by:
- involving the units in the Bank’s Risk Management Area or the Bank’s relevant committees in evaluating large transactions of the Group entities;
- giving opinions and reviewing internal regulations concerning risk management in the individual Group entities, carried out by the units in the Bank’s Risk Management Area;
- reporting on the Group entities’ risks to the Bank’s relevant committees or the Management Board;
- monitoring of strategic risk tolerance limits for the Group.
The PKO Bank Polski SA Group’s top priority is to maintain its strong capital position and to further increase its stable sources of financing underlying the stable development of business activity, while maintaining the priorities of efficiency and effective cost control and appropriate risk assessment.
In this respect, the Bank took the following actions in 2014:
- in January 2014, acquired financing due to issuance of bonds under the EMTN programme in the amount of EUR 500 million,
- in February 2014, acquired financing due to Cross Currency Repo transactions in the amount of CHF 50 million,
- in April 2014, acquired long-term financing from Nordea AB in the amount of PLN 14 billion (described in the note 25 ‘Investments in associates and joint ventures’),
- in May and November 2014, rolled forward short-term bonds with a current maturity of three months in the amount of PLN 700 million and issued additional PLN 50 million of these securities,
- transferred a part of the Bank's profit for 2013 and a part of the Bank’s net profit for 2014, after deducting the expected charge and dividends, based on the decision of the Polish Financial Supervision Authority, to own funds.
The acquisition of Nordea Polska entities as at 1 April 2014 and the legal merger as at 31 October 2014 had no impact on the change in the risks identified in the business of the Group.
In October 2014, PKO Bank Polski SA obtained the Polish Financial Supervision Authority’s consent to introduce a significant expansion of the AMA approach used for calculating the own funds requirement in respect of operating risk, by including in this approach an additional part of the operations which resulted from the legal merger.
In 2014 in respect of operational risk, the Bank endeavoured to ensure that after the legal merger the Bank will be adapted to the requirements of Recommendation M of the Polish Financial Supervision Authority amended in January 2013 relating to operational risk management in banks.
52.5. Identification of significant types of risk
The significance of the individual types of risk is established at the Bank’s and the Group entities level. When determining criteria of classifying a given type of risk as significant, an influence of a given type of risk on the Bank’s, the Group entities and the whole Group’s activities is taken into account, whereas three types of risk are recognised:
- considered as significant a priori – being managed actively,
- potentially significant – for which significance monitoring is being made,
- other non-defined or non-occurring in the Bank or in the Group types of risk (insignificant and non-monitored).
Based on quantitative and qualitative information, an assessment of significance of potentially significant types of risk is performed in the Bank periodically. As a result of assessment, a given type of risk is being classified as significant/insignificant. Similar assessment is concluded periodically in the Group entities. Monitoring is conducted if significant change in activities took place or the profile of the Bank or the Group entities have changed.
